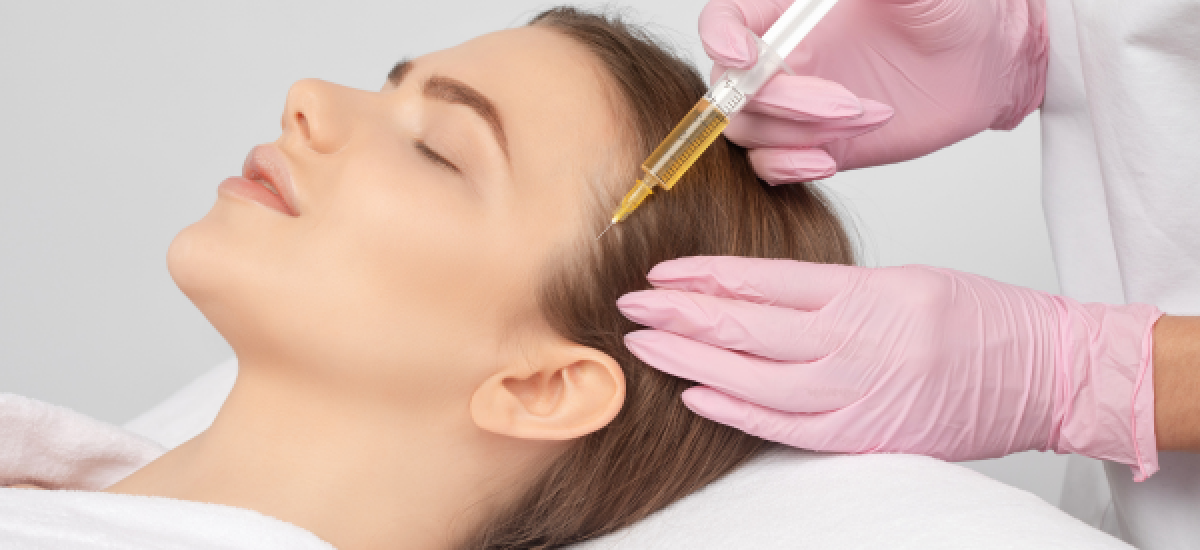
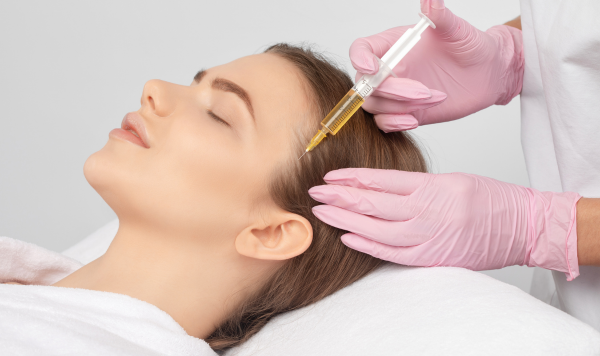
PRP Therapy, or Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy, is a medical treatment that involves injecting a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to accelerate the healing of injured tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints. PRP is derived from a sample of the patient’s blood, which is processed to increase the concentration of platelets. These platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate and enhance the healing process.
How PRP Therapy Works:
- Blood Collection: A small amount of blood is drawn from the patient.
- Processing: The blood is placed in a centrifuge to separate the platelets from the other blood components.
- Injection: The concentrated platelet-rich plasma is injected directly into the injured or affected area.
Common Uses:
- Orthopedics: To treat injuries such as tendonitis, ligament sprains, and osteoarthritis.
- Aesthetics: For facial rejuvenation and hair restoration.
- Sports Medicine: To accelerate recovery from sports-related injuries.